Preamble
Imagine you want to search a word in a dictionary, what will you do? open it from the first until you find the word? of course it will take a lot of time.
Or maybe you will open it from the middle. If the word is on the left side, you will open the left side; if the word is on the right side, you will open the right side, and so on. This is faster, right?
The first method is called linear search or simple search, and the second method is what we call as binary search.
There is a requirement to using a binary search, which is the list should be sorted, otherwise it will not work.
Linear Search
.webp)
source: Geeks for Geeks - Linear Search
In Linear Search, we will check the value item by item starting from the first element until we find the target value.
Example Code
Let’s say we have an array of numbers and we want to search a number in the array. I will use JavaScript for the example.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
function linearSearch(list, target) {
let count = 0; // loop counter
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (list[i] === target) {
console.log('Loop count:', count); // log the loop counter
return i;
}
count++; // increment the loop counter
}
console.log('Loop count:', count); // log the loop counter
return -1;
}
In the example above, if you have a list of 1000 items and you want to search for the last number, the loop will execute 1000 times.
In Big O notation, the time complexity of linear search is O(n), where n is the number of elements in the list.
Okay, now we understand how linear search works and how long it will take to search a number in a list. Let’s move to the binary search.
Binary Search
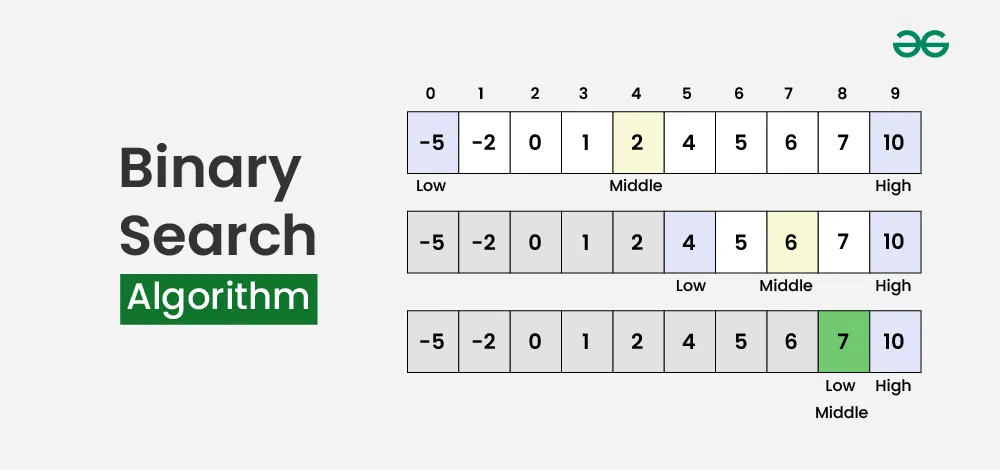
source: Geeks for Geeks - Binary Search
In Binary Search, we will check the middle value of the list. If the target value is less than the middle value, we will search in the left side of the middle value, otherwise we will search in the right side of the middle value.
Example Code
We will use JavaScript for the example.
-
First we prepare the array of numbers and an empty function.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]; function binarySearch(list, target) { // code here... } -
Then we will implement the binary search algorithm by creating 3 variables:
left,right, andmiddle.const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]; function binarySearch(list, target) { let left = 0; let right = list.length - 1; let middle = Math.floor((left + right) / 2); }leftis the index of the first element in the list.rightis the index of the last element in the list.middleis the index of the middle element in the list.
-
Next, we will create a loop to check if the target is in the left side or the right side of the middle. If the target is in the left side, we will update the
rightvariable to be themiddle - 1, if the target is in the right side, we will update theleftvariable to be themiddle + 1and the loop will continue until the target is found in the middle index.const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]; function binarySearch(list, target) { let left = 0; let right = list.length - 1; let middle = Math.floor((left + right) / 2); // start here... while (left <= right) { if (list[middle] === target) { return middle; } else if (list[middle] < target) { left = middle + 1; } else { right = middle - 1; } middle = Math.floor((left + right) / 2); } return -1; } -
Then we can add few console.log to see how many times the loop is executed.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]; function binarySearch(list, target) { let left = 0; let right = list.length - 1; let middle = Math.floor((left + right) / 2); // new loop counter let count = 0; while (left <= right) { // increment the loop counter count++; if (list[middle] === target) { // log the loop counter console.log('Loop count:', count); return middle; } else if (list[middle] < target) { left = middle + 1; } else { right = middle - 1; } middle = Math.floor((left + right) / 2); } // log the loop counter console.log('Loop count:', count); return -1; } console.log(binarySearch(numbers, 5)); // 4
In the example above, if you have a list of 1000 items and you want to search for the last number, the loop will execute 10 times.
In Big O notation, the time complexity of binary search is O(log n), where n is the number of elements in the list.
Online Playground
you can try run:
npm run linearfor linear searchnpm run binaryfor binary search
take a look at the terminal to see how many times the loop is executed for each search.
Conclusion
Binary search is a very efficient algorithm to search an element in a sorted list. It is faster than linear search because it reduces the number of comparisons in each iteration.
The time complexity of binary search is O(log n), which is much faster than linear search with O(n).
That’s all about binary search, I hope you understand how it works and how to implement it in your code. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comment section below.
Credits
- Thanks to Indonesia Belajar for such a great explanation about Data Structure and Algorithm.
- Thanks to Geeks for Geeks for the images.
- Thanks to Github Copilot 🤖 also.
Happy coding! 🚀